Appendix H. Audit Act 1994 section 16–submissions and comments
In accordance with section 16(3) of the Audit Act 1994 a copy of this report, or relevant extracts from the report, was provided to the Department of Treasury and Finance, the Department of Sustainability and Environment, the Essential Services Commission, VicWater and the 20 entities with a request for submissions or comments.
The submission and comments provided are not subject to audit nor the evidentiary standards required to reach an audit conclusion. Responsibility for the accuracy, fairness and balance of those comments rests solely with the agency head.
Appendix G. Performance indicators
This Appendix sets out the performance indicators against which water entities are required to report.
Financial Reporting Direction 27B Presentation and Reporting of Performance Information specifies the entities required to prepare and submit for audit a performance report. Ministerial directives issued under section 51 of the Financial Management Act 1994 specify the performance indicators that need to be reported in a performance report.
Financial indicators
Indicator |
|---|
Appendix F. Entity level financial sustainability
Indicators of financial sustainability
This Appendix sets out the financial indicators used in this report. The indicators should be considered collectively, and are more useful when assessed over time as part of a trend analysis. The indicators have been applied to the published financial information of the 19 water entities for the five-year period 2007–08 to 2011–12.
Appendix E. Financial composition
This Appendix presents the composition of revenue, expenses, assets and liabilities at an industry, metropolitan, regional urban and rural level.
Industry level
Figure E1
Revenue composition
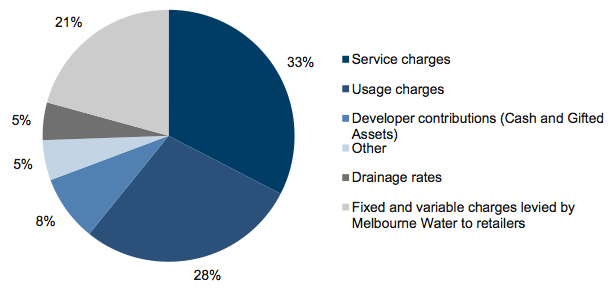
Source: Victorian Auditor-General’s Office.
Figure E2 Expense composition
Appendix D. Audit status
Metropolitan
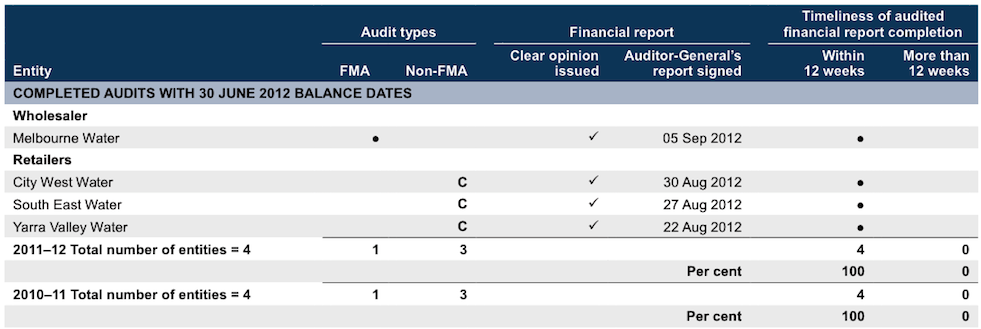
Note: Non-FMA audit types: C – Corporations Act 2001.
The performance report for Melbourne Water was completed on the same date as the financial report. A clear opinion was issued.
Source: Victorian Auditor-General’s Office.
Appendix C. Reports on the results of the 2011–12 financial audits
Reports
This report is the third of six reports to be presented to Parliament covering the results of our audits of public sector financial reports. The reports in this series are outlined in Figure C1.
Figure C1
VAGO reports on the results of the 2011–12 financial audits
Report |
Description |
|---|---|
Auditor-General’s Report on the Annual Financial Report of the State of Victoria, 2011–12 |
Appendix B. Accountability arrangements
Governance
The responsible minister for the water industry is the Minister for Water. The relationship between the Minister for Water and the water entities is established by the Water Act 1989.
The Water Group, a business unit within the Department of Sustainability and Environment, supports and advises the Minister for Water.
The 19 water entities also report to the Treasurer of Victoria.
Appendix A. Acronyms and glossary
Acronyms
AAS Australian Accounting Standard
AASB Australian Accounting Standards Board
DSE Department of Sustainability and Environment
ESC Essential Services Commission
FMA Financial Management Act 1994
FRD Financial Reporting Direction
VAGO Victorian Auditor-General's Office
6 Internal controls
At a glance
Background
This Part presents the results of our assessment of general internal controls and controls over risk management and water tariff revenue.
Conclusion
Internal controls were adequate for producing reliable, materially accurate and timely financial reports. Nevertheless, a number of areas for improvement were identified.